Appearance
SDK Concept and functional description
The SingularityNET Platform SDK is designed to provide a convenient programming interface for application developers:
- It enables integration of a wide variety of AI models into applications.
- It also allows exposing these capabilities directly to end‑users.
The SDK protocol defines the overall structure, entities, and functionality of the SingularityNET Platform SDK, independent of the specific implementation language.
While internal structure and entities may differ between language implementations, all SDKs must remain compatible and consistently expose interfaces to the essential platform components.
User Flow
Note: This section includes mandatory requirements for implementation.
This is a general scenario for an SDK user.
Preparatory actions
- Creating a
Configinstance with the required values. - Creating a
SNETEngineinstance with the config passed to it. - Adding a new account (wallet) (
Account) to the engine by calling aSNETEnginemethod (optional, but in most cases needed). - Creating a new
ServiceClientinstance by calling aSNETEnginemethod (optional, but in most cases needed).
Once these steps are done, the SDK functionality becomes available through the SNETEngine and ServiceClient instances.
ServiceClient functionality
CallPaymentChannel— functions of the MPE contract for the channel (e.g.add funds,extend expiraton)ServiceMetadata— functions for editing service metadata, as well as for publishing metadata to metadata provider, and downloading metadata from it
SNETEngine functionality
Channels— functions of the MPE contract for the set of channels (e.g.open channel,load channels)MPEContract— functions of the MPE contract for the account (e.g.claim,deposit) (in fact, MPEContract contains all the functionality of MPE, but access to other functions is more convenient in other ways (through other entities))RegistryContract— functions of the Registry contract for services and organizationsMetadataProvider→OrgMetadata— functions for editing organization metadata, as well as for publishing metadata to metadata provider, and downloading metadata from it
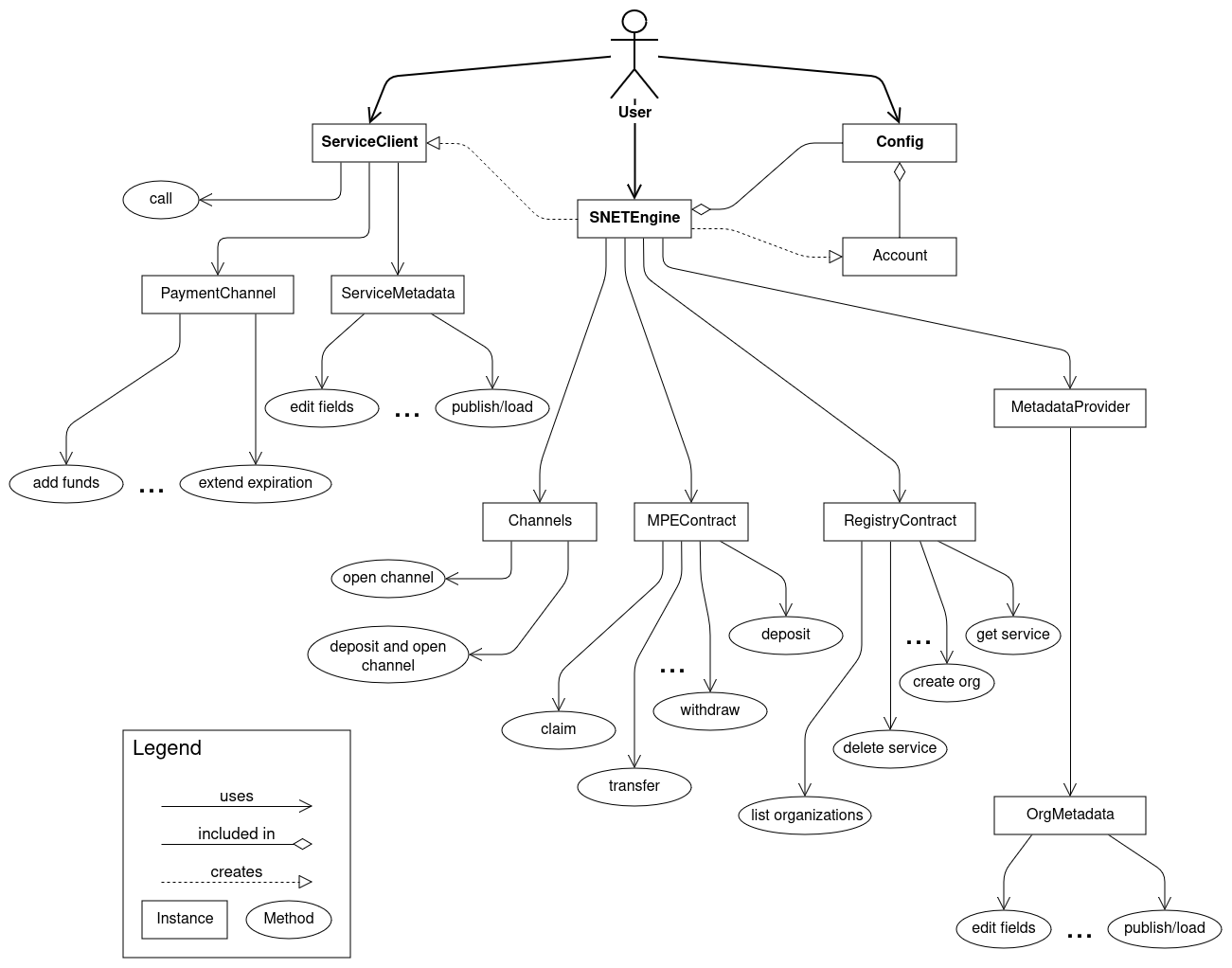
Structure
Note: The presented structure is just one possible implementation. It doesn't have to be followed in its entirety, but it's worth using as an example.
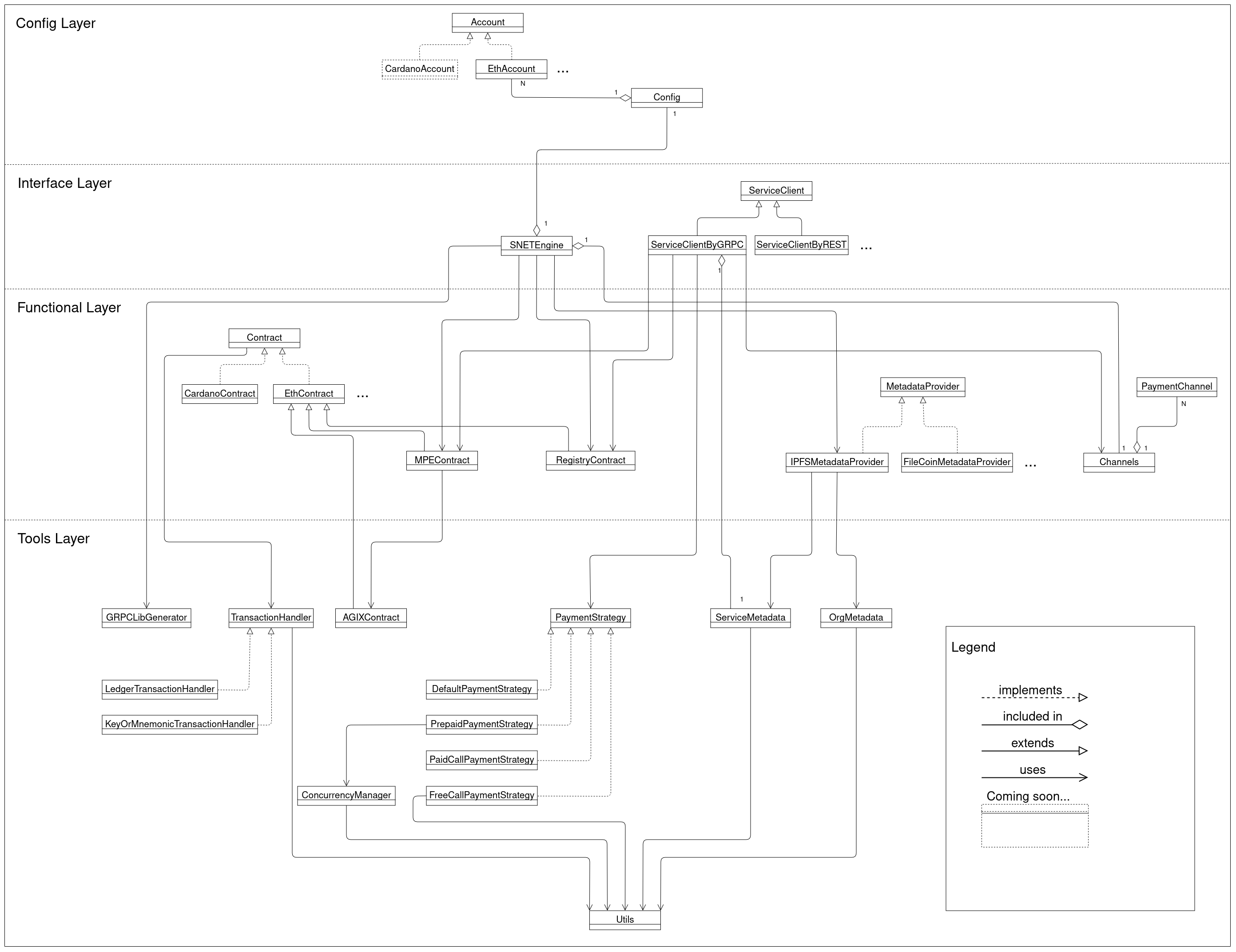
All entities can be divided into 4 layers:
Config Layercontains entities with many fields, that are needed to configure SDK.- At
Interface Layerthere are entities through which users have access toFunctional Layer. Functional Layercontains in its entities all the functionality of the SDK that users may need.Tools Layercontains entities with various auxiliary functionality required for the operation of the functional level.
Entities
Note: The presented structure and entities is just one possible implementation. It doesn't have to be followed in its entirety, but it's worth using as an example.
Config Layer
Account
Account is an abstract entity. It's the base entity to EthAccount and others that are planned to be implemented to work with other blockchains on the SNET platform.
EthAccount
EthAccount implements Account. It is needed to identify user wallet in the Ethereum blockchain. It contains all the fields, that need to be known for it to work correctly (e.g. private key, mnemonic phrase, wallet address etc.). Its instance is created using a name, account type (key, mnemonic or ledger) and corresponding secret, the remaining fields are initialized automatically by Web3 by default. Contains almost no logic, only account data.
Data
- name
- address
- account type
- private key (optional)
- mnemonic phrase (optional)
- index (optional)
- nonce
Functionality
- address determination by key/mnemonic/ledger by using Web3
- updating the nonce value and comparison it with the value received via Web3
Config
Config is the main configuration entity containing all the data needed to work in the SNET platform. It contains entry point, network name, blockchain type, smart contract addresses (optional) and some other options. These values are specified when creating an instance, which is then passed to SNETEngine.
Data
- blockchain entry point
- blockchain type
- network name
- accounts (list/map)
- MPE, Registry, AGIX contracts addresses (optional)
- forced update protobuf files (bool) (optional)
- concurrency (bool) (optional)
Functionality
- adding an account
- getting an account
Interface Layer
SNETEngine
SNETEngine is the most important entity from the user side. Config's instance is installed in it, and new accounts and service clients are created by using it. SNETEngine creates and contains instances of almost all entities from Functional Layer (MPEContract, RegistryContract, MetadatProvider etc.), so they are accessed through it, and therefore most of the SDK functions are accessible from SNETEngine.
Data
Config's instance- an instance of a Web3 library entity that will be passed to all dependent entities
MPEContract's instanceRegistryContract's instanceAGIXContract's instance- an instance of the metadata provider implementation
GRPCLibGenerator's instanceChannels's instance
Functionality
- creating new
Account - creating and initializing new
Service - providing the user with access to
MPEContract's instance or to its functionality - providing the user with access to
RegistryContract's instance or to its functionality - providing the user with access to
AGIXContract's instance or to its functionality - providing the user with access to metadata provider or to its functionality
ServiceClient
Service is an entity that allows an account to call a service and also call contracts and metadata provider functionality related on service. It contains the most important abstract method call for calling a service with given parameters. It's the base entity to ServiceClientByGRPC and others that are planned to be implemented to access daemons using other methods, such as REST API.
Data
- organization id
- service id
- payment group
- service metadata
- payment strategy
Account's instance (it's got from the owner's entitySNETEngine)Channels's instance (it's got from the owner's entitySNETEngine)MPEContract's instance (it's got from the owner's entitySNETEngine)RegistryContract's instance (it's got from the owner's entitySNETEngine)- an instance of the metadata provider implementation (it's got from the owner's entity
SNETEngine) - an instance of a Web3 library entity (it's got from the owner's entity
SNETEngine)
Functionality
- call a service with given parameters (abstract)
- providing the user with access to
MPEContract's instance functionality related on channels - providing the user with access to
RegistryContract's instance functionality related on services - providing the user with access to metadata provider functionality related on service metadata
- getting service information
ServiceClientByGRPC
ServiceClientByGRPC extends ServiceClient. It allows you to call service functions by communicating with the daemon via gRPC
Data
- grpc channel
- data needed for grpc call
- protobuf modules
Functionality
- implementation of a service call with given parameters via gRPC
Functional Layer
Contract
Contract is an abstract entity. It contains abstract methods to call read and write functions of smart contracts. It's the base entity to EthContract and others that are planned to be implemented to work with other blockchains on the SNET platform.
EthContract
EthContract implements Contract. It allows you to call read functions and perform transactions for calling write functions of smart contracts in Ethereum. EthContract is the base entity for MPEContract, RegistryContract and AGIXContract.
Data
- an instance of a Web3 library entity (it's got from the owner's entity
SNETEngine) - smart contract object from Web3 library
- contract address
Functionality
getting Web3 library contract object by name and optionally address (using
snet.contractslibrary)getting contract info from Web3 library contract object
calling contract read functions by name and parameters
calling contract write functions by name and parameters and execution of the entire transaction pipeline:
- building transaction
- signing transaction (using
TransactionHandler) - sending transaction (using
TransactionHandler) - processing transaction result
getting and increasing gas price to efficiently execute a transaction on the blockchain using the following algorithm (in Python)
python
def _get_gas_price(self):
gas_price = self.w3.eth.gas_price
if gas_price <= 15000000000:
gas_price += gas_price * 1 / 3
elif 15000000000 < gas_price <= 50000000000:
gas_price += gas_price * 1 / 5
elif 50000000000 < gas_price <= 150000000000:
gas_price += 7000000000
elif gas_price > 150000000000:
gas_price += gas_price * 1 / 10
return int(gas_price)MPEContract
MPEContract extends EthContract. It's an entity that provides all the functionality from MultyPartyEscrow Contract.
Data
AGIXContract's instance (it's got from the owner's entitySNETEngine)
Functionality
calling read functions:
- balance
- channels
calling write functions:
- deposit
- openChannel
- channelExtendAndAddFunds
- etc.
Using
AGIXContractin functions where it is needed
RegistryContract
RegistryContract extends EthContract. It's an entity that provides all the functionality from Registry Contract.
Functionality
calling read functions:
- getOrganizationById
- getServiceRegistrationById
- etc.
calling write functions:
- createOrganization
- updateServiceRegistration
- etc.
MetadataProvider
MetadataProvider is an abstract entity. It allows you to keep (save and get) organization and service metadata (and by the way also .proto files). It's the base entity to IPFSMetadataProvider and others that are planned to be implemented to work with other external file storages on the SNET platform.
Functionality
- getting organization metadata from external storage (abstract)
- getting service metadata from external storage (abstract)
- getting
.protofiles from external storage (abstract) - publishing organization metadata in external storage (abstract)
- publishing service metadata in external storage (abstract)
- publishing
.protoin from external storage (abstract)
IPFSMetadataProvider
IPFSMetadataProvider implements MetadataProvider. It allows you to work with metadata and .proto files using Interplanetary Filesystem (IPFS).
Data
RegistryContract's instance (it's got from the owner's entitySNETEngine)- an instance of a IPFS HTTP client entity from the corresponding library
- directory for storage protobuf files
Functionality
- implementation of parent methods for IPFS
- converting hash to URL (bytes) and back
PaymentChannel
PaymentChannel is an entity that stores information about an open channel and allows the functions provided by MPE to be performed on it.
Data
- channel id
- an instance of a Web3 library entity (it's got from the owner's entity
Channels) - account
MPEContract's instance (it's got from the owner's entityChannels)- channel state
Functionality
MPE functions applied to account and channel data, such as:
- addFunds
- extendExpiration
- etc.
channel state synchronization with MPE
Channels
Channels is an entity that stores set of PaymentChannels and allows services to interact with them effectively.
Data
- channels (list/map)
- an instance of a Web3 library entity (it's got from the owner's entity
SNETEngine) MPEContract's instance (it's got from the owner's entitySNETEngine)- MPE deployment block
Functionality
storing channels information (
PaymentChannels)search for channels in blockchain
MPE functions applied to channels, such as:
- openChannel
- etc.
Tools Layer
GRPCLibGenerator
GRPCLibGenerator is an entity needed to generate stub files in a specific language.
Data
IPFSMetadataProvider's instance (it's got from the owner's entitySNETEngine)RegistryContract's instance (it's got from the owner's entitySNETEngine)
Functionality
generation of
stubfiles based on specified organization and service ids, including:- getting service metadata from Registry
- getting
.protofile from IPFS - compiling
.protofile tostubfile and saving it in a given directory
AGIXContract
AGIXContract extends EthContract. It's an entity that provides the functionality from SingularityNET AGIX Token Contract.
Functionality
calling read functions:
- allowance
- balanceOf
- etc.
calling write functions:
- approve
- transfer
- etc.
ServiceMetadata
ServiceMetadata is an entity for manipulating service metadata. It is possible that there may be other entities inside for complex metadata fields. Below is an example of service metadata.
json
{
"version": 1,
"display_name": "Example service",
"encoding": "proto",
"service_type": "grpc",
"model_ipfs_hash": "QmeyrQkEyba8dd4rc3jrLd5pEwsxHutfH2RvsSaeSMqTtQ",
"mpe_address": "0x7E0aF8988DF45B824b2E0e0A87c6196897744970",
"groups": [
{
"free_calls": 0,
"free_call_signer_address": "0x7DF35C98f41F3Af0df1dc4c7F7D4C19a71Dd059F",
"daemon_addresses": [
"0x0709e9b78756b740ab0c64427f43f8305fd6d1a7"
],
"pricing": [
{
"default": true,
"price_model": "fixed_price",
"price_in_cogs": 1
}
],
"endpoints": [
"http://node1.naint.tech:62400"
],
"group_id": "/mb90Qs8VktxGQmU0uRu0bSlGgqeDlYrKrs+WbsOvOQ=",
"group_name": "default_group"
}
],
"service_description": {
"url": "https://ropsten-v2-publisher.singularitynet.io/org",
"short_description": "Example service",
"description": "Example service"
},
"media": [
{
"order": 1,
"url": "https://ropsten-marketplace-service-assets.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/samples/services/d05c62bf9aa84843a195457d98417f4e/assets/20240327124952_asset.jpeg",
"file_type": "image",
"asset_type": "hero_image",
"alt_text": ""
}
],
"contributors": [
{
"name": "test",
"email_id": ""
}
],
"tags": [
"calculator"
]
}Data
- map (or just fields) with service data
Functionality
- updating fields value
- adding new data to fields that are lists (media, groups, etc.)
- removing data from fields that are lists (media, groups, etc.)
- converting from
jsonand back
OrgMetadata
ServiceMetadata is an entity for manipulating organization metadata. It is possible that there may be other entities inside for complex metadata fields. Below is an example of organization metadata.
json
{
"org_name": "Snet_test",
"org_id": "samples",
"org_type": "individual",
"description": {
"description": "Snet_test",
"short_description": "Snet_test",
"url": "https://ropsten-v2-publisher.singularitynet.io"
},
"assets": {
"hero_image": "QmfTjcwBYwWCp5hdC5E3DRyHBFafaCVHDs1cCammDYkQPE/20240327124724_asset.jpeg"
},
"contacts": [
{
"email": "",
"phone": "+18005551234",
"contact_type": "general"
},
{
"email": "test@gmail.com",
"phone": "+18005551234",
"contact_type": "support"
}
],
"groups": [
{
"group_name": "default_group",
"group_id": "/mb90Qs8VktxGQmU0uRu0bSlGgqeDlYrKrs+WbsOvOQ=",
"payment": {
"payment_address": "0x0709e9B78756B740ab0C64427f43f8305fD6D1A7",
"payment_expiration_threshold": 40320,
"payment_channel_storage_type": "etcd",
"payment_channel_storage_client": {
"connection_timeout": "5s",
"request_timeout": "3s",
"endpoints": [
"https://127.0.0.1:2379"
]
}
}
}
]
}Data
- map (or just fields) with organization data
Functionality
- updating fields value
- adding new data to fields that are lists (groups, contacts, etc.)
- removing data from fields that are lists (groups, contacts, etc.)
- converting from
jsonand back
TransactionHandler
TransactionHandler is an abstract entity. It allows you to conduct transactions. TransactionHandler is the base entity to LedgerTransactionHandler and KeyOrMnemonicTransactionHandler.
Functionality
- signing transaction
- sending transaction
- getting wallet address
- signing message
LedgerTransactionHandler
LedgerTransactionHandler implements TransactionHandler. It allows you to conduct transactions using ledger.
Data
- address
- index
- dongle path
Functionality
- connecting to ledger
KeyOrMnemonicTransactionHandler
KeyOrMnemonicTransactionHandler implements TransactionHandler. It allows you to conduct transactions using key or mnemonic with index.
Data
- private key
- address
Functionality
- implementation parent's functionality using Web3
PaymentStrategy
PaymentStrategy is an abstract entity. It's needed for execution of various types of payments. PaymentStrategy is the base entity to DefaultPaymentStrategy, FreeCallPaymentStrategy, FreeCallPaymentStrategy and PaidCallPaymentStrategy.
Functionality
- getting call price (abstract)
- getting payment metadata (abstract)
DefaultPaymentStrategy
DefaultPaymentStrategy implements PaymentStrategy. This payment strategy is used by default when the user does not specify which strategy to use. And in fact, this is not a separate strategy, this entity, depending on various conditions, chooses strategy from FreeCallPaymentStrategy, FreeCallPaymentStrategy and PaidCallPaymentStrategy.
Data
ConcurrencyManager's instance- channel
Functionality
- choosing payment strategy
FreeCallPaymentStrategy
FreeCallPaymentStrategy implements PaymentStrategy. This payment strategy can be used when the user has free service call tokens.
Functionality
- checking for free call tokens
- implementation of parent's functionality for free-call type of call
PrepaidPaymentStrategy
PrepaidPaymentStrategy implements PaymentStrategy. This strategy can be used when the user has deposited funds into the channel in advance and wants to pay for several calls at once.
Data
ConcurrencyManager's instance (it's got from the owner's entity, usually fromDefaultPaymentStrategy)- call allowance
- block offset (240 by default)
Functionality
- providing concurrency
- implementation of parent's functionality for prepaid type of call
- selecting channel with checking for its presence, amount and expiration
PaidCallPaymentStrategy
FreeCallPaymentStrategy implements PaymentStrategy. This payment strategy can be used when the user wants to call the service once.
Data
- call allowance
- block offset (240 by default)
Functionality
- implementation of parent's functionality
- selecting channel with checking for its presence, amount and expiration
ConcurrencyManager
ConcurrencyManager is an entity that organizes and controls concurrency by turning to the daemon.
Data
- amount of concurrent calls
- token
- planned and used amount
Functionality
- working with channel
- getting token from daemon
- control of planned and used funds
Utils
Utils is an entity that contains a set of functions used in many other entities.
Functionality
- validation of URL
- validation of endpoint
- getting address from private key and mnemonic
- getting data from abi
- etc.
Interfaces
Note: This section includes mandatory requirements for implementation.
Smart Contracts
Payment for service calls on the Singularity NET platform is made using the Singularity NET Token (AGIX) through a payment channel. To realize a service call on the platform, there are smart contracts. Each of them is responsible for a specific functionality.
MultiPartyEscrow
The main purpose of MPE is to manage payment channels. For a call to be successful, a suitable payment channel must be open, it must have sufficient funds and it must not be overdue. MPE is needed to manage this and monitor the channels.
Here are the functions of this contract that the SDK must be able to call
balances- returns MPE balancechannels- returns the channel's stateopenChannel- opens a new channel with a given amount of funds and expirationchannelAddFunds- adds funds to the channelchannelExtend- extends the expiration of the channelchannelExtendAndAddFunds- extends the expiration of the channel and adds fundsdeposit- deposits funds into the MPEdepositAndOpenChannel- deposits funds into the MPE and opens a new channel with the same amount of funds and a given expirationwithdraw- withdraws funds from the MPE back to the walletchannelClaim- claims funds from the channel (for the service providers)multiChannelClaim- claims funds from multiple channels (for the service providers)channelClaimTimeout- claims funds from the channel if the channel has expired (for the service consumers)
You can see the implementation of MultiPartyEscrow in Ethereum here.
Registry
Registry is designed to manage data about organizations and services, as well as their metadata. With its help you can register an organization and a service, as well as get URI to their metadata in storage providers (and from the service metadata you can get a URI to the service API).
Here are the functions of this contract that the SDK must be able to call
getOrganizationById- returns organization datagetServiceRegistrationById- returns service URIlistOrganizations- returns list of organization IDslistServicesForOrganization- returns list of service IDs for an organizationcreateOrganization- creates an organizationdeleteOrganization- deletes an organizationcreateServiceRegistration- creates a servicedeleteServiceRegistration- deletes a serviceupdateServiceRegistration- updates service metadata URIaddOrganizationMembers- adds members to the organizationremoveOrganizationMembers- removes members from the organizationchangeOrganizationMetadataURI- changes organization metadata URIchangeOrganizationOwner- changes organization owner
You can see the implementation of Registry in Ethereum here.
SingularityNetToken
The AGIX Token is an ERC-20 token that powers the SingularityNet platform. In the SDK, this contract is needed to check the balance and deposit funds into the MPE
Here are the functions of this contract that the SDK must be able to call
balanceOf- returns balance of the walletallowance- returns the allowance for spendingapprove- approves a spender (particularly MPE) to take a certain amount of your funds
You can see the implementation of SingularityNET AGIX Token in Ethereum here
Storage Providers
The storage provider is designed to store metadata of services and organizations, as well as services (daemons) APIs. Organization and service metadata URI are stored in Registry. Service API source (URI) is stored in service metadata in the field service_api_source.
URI is a string consisting of a prefix with the name of the storage and the identifier of the file in that storage <STORAGE_NAME>://<FILE_IDENTIFIER>. The organization and service metadata URIs stored in the registry are additionally encoded in ASCII format and padded with null bytes.
IPFS
URI example: ipfs://<IPFS_HASH>
FileCoin
URI example: filecoin://<FILECOIN_CID>
Daemon
Interaction with the daemon is currently carried out only using gRPC. To call the service, you need to get the service API (.proto files) from the storage provider, compile them and call any of the described methods via gRPC. In addition, the daemon has methods that are the same for everyone. Therefore, the SDK stores .proto files for the following services, which are the same for all daemons:
state_service- needed to determine the current state of the channelcontrol_service- needed to change the configuration of the daemontoken_service- needed for concurrency implementationtraining- needed to work with AI models
Implementations
The SingularityNET SDK is currently available in two fully supported languages:
Two more SDKs are under active development:
All SDK implementations follow the same overall design principles and strategy.
Note: According to the design pattern, core SDK functionality must be consistently available across all programming languages (e.g., Python, WebJS).
The SDK provides several default funding strategies for payment channels, while also allowing developers to implement their own strategies to maintain full control over tokens and service payments.
Together with the CLI, the SDK simplifies the process of fetching the latest service specifications, compiling proto definitions, and invoking services with minimal setup.
- A fully functional Python SDK is available (see design improvement issues).
- A fully functional WebJS SDK is also available.
Work is ongoing on the Node.js SDK and the Java SDK. Support for other popular languages is planned, and community contributions are welcome.
