Appearance
Hosting-as-a-Service (HaaS)
What is HaaS?
Hosting-as-a-Service (HaaS) is a managed infrastructure solution that eliminates the need to deploy and maintain your own daemon instances. Instead of handling installation, environment setup, and server provisioning manually, you provide your service configuration, and the platform automatically provisions, deploys, and manages the daemon for you.
Each HaaS deployment runs in an isolated, containerized environment with:
- Dedicated virtual machine
- Pre-configured runtime environment
- Automated daemon deployment and lifecycle management
- Built-in payment channel storage (ETCD)
- Automated infrastructure updates and maintenance
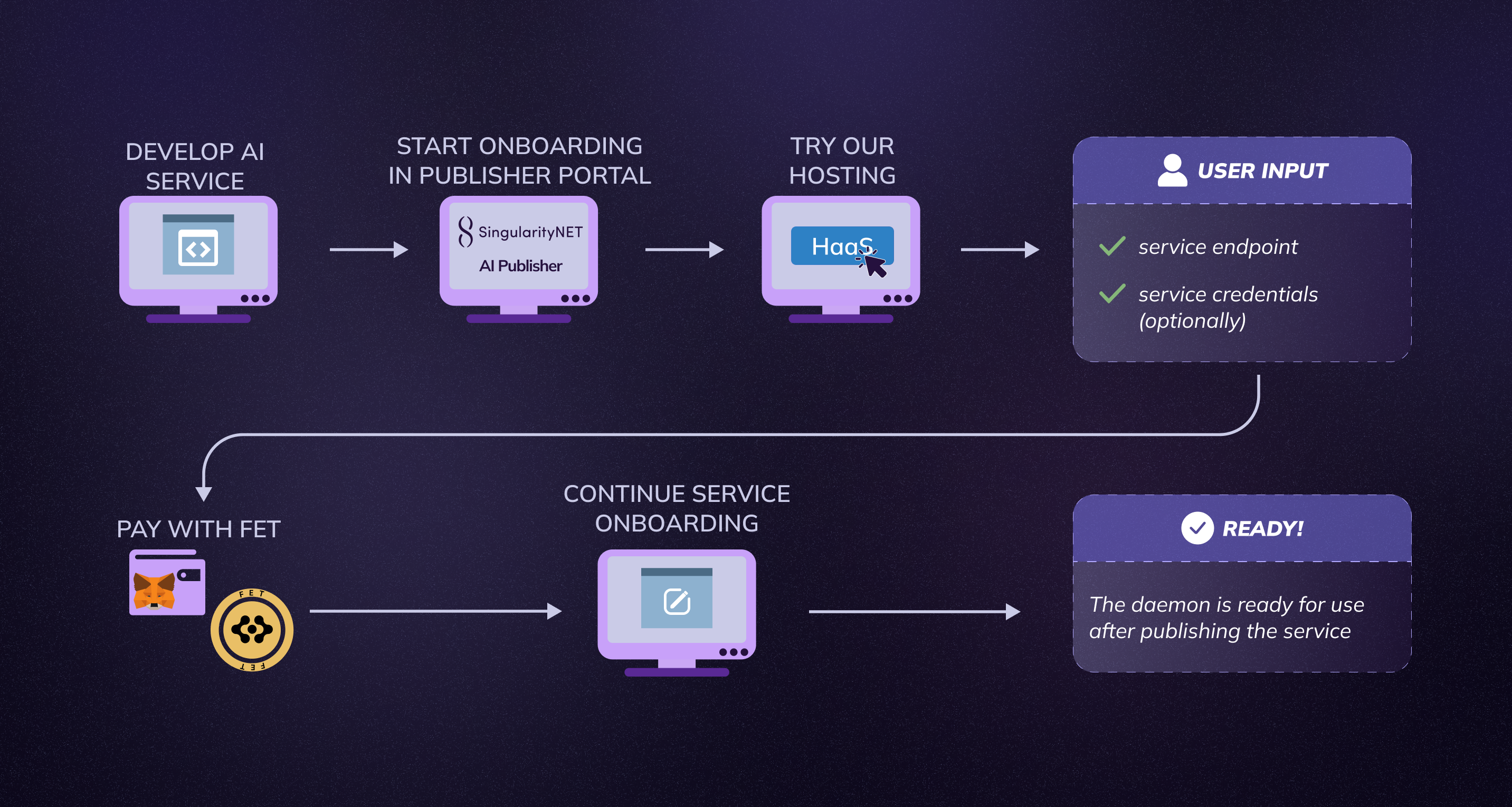
Complete HaaS deployment process from development to production
HaaS vs Self-Hosted Daemon
Choose the deployment method that best fits your needs:
| Aspect | HaaS (Managed) | Self-Hosted Daemon |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Setup | ✅ Fully automated | ⚠️ Manual configuration required |
| Server Management | ✅ Managed by platform | ❌ You maintain servers |
| ETCD Configuration | ✅ Pre-configured | ⚠️ Manual setup required |
| SSL Certificates | ✅ Handled automatically | ⚠️ You manage certificates |
| Updates & Maintenance | ✅ Automatic | ❌ Manual updates |
| Technical Expertise | Beginner-friendly | Advanced |
| Cost Structure | Monthly subscription (FET tokens) | Infrastructure costs only |
| Scalability | ✅ Easy scaling | ⚠️ Manual scaling |
When to Use HaaS
Choose HaaS if:
- You want to focus on AI service development, not infrastructure
- You need quick deployment without server management
- You prefer predictable monthly costs
- You don't want to handle ETCD, SSL, or daemon configuration
- You need reliable uptime with automated maintenance
When to Use Self-Hosted Daemon
Choose Self-Hosted if:
- You need full control over infrastructure
- You have existing server infrastructure
- You want to minimize recurring costs
- You require custom daemon configurations
- You have DevOps expertise
For self-hosted deployment instructions, see the Full Onboarding Guide.
Prerequisites
Before deploying with HaaS, ensure you have:
- Service Created (Not Published): Your service must be created through the Publisher Portal (Steps 1 and 2 completed) but NOT yet published to the blockchain. Once a service is published, HaaS deployment will no longer be available for that service.
- AI Service Running: Your actual AI service must be deployed and accessible via HTTP/HTTPS endpoint
- MetaMask Wallet: With sufficient FET tokens for monthly subscription payment
- Service Endpoint: Public URL where your AI service is accessible (e.g.,
https://your-service.example.com) - Authorization (optional): Key, value, and location for each authorization parameter if your service requires authentication
Naming Requirements
When creating your service (Steps 1 and 2), ensure your Organization ID and Service ID follow these rules:
- Lowercase only: Use only lowercase letters (a-z)
- Allowed characters: Letters, numbers, and hyphens (
-) - No special characters: Do not use uppercase letters, underscores, spaces, or other special characters
Valid examples:
- Organization ID:
my-company,acme-corp,ai-services,test-org - Service ID:
image-classifier,sentiment-analysis,translation-api,test-service
Invalid examples:
- ❌
MyCompany(uppercase) - ❌
test_service(underscore) - ❌
AI Services(space and uppercase)
Deploying Your Daemon with HaaS
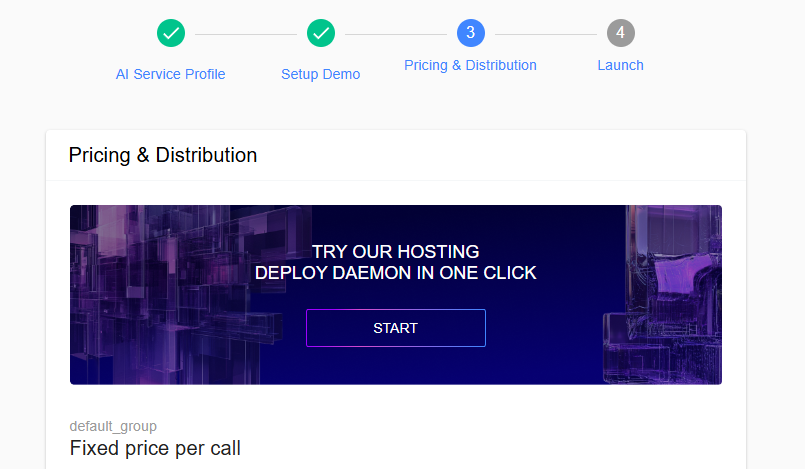
Step 1: Access HaaS During Service Creation
After completing the first two steps of service creation in the Publisher Portal, you'll see the daemon configuration step. At the top of this page, you'll find:
"TRY OUR HOSTING
DEPLOY DAEMON IN ONE CLICK"
Click this section to open the HaaS setup wizard.
Step 2: Configure Daemon Hosting
The Daemon Hosting Payment modal will appear with the following fields:
Required Configuration
| Field | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly Cost | Subscription price in FET tokens (displayed automatically) | TBD FET/month |
| Service Endpoint | Public URL where your AI service is running | https://api.yourservice.com |
Optional Configuration
| Field | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Authorization | Key, value, and location for each authorization parameter if your service requires authentication | Key: Authorization, Value: Bearer token123, Location: header |
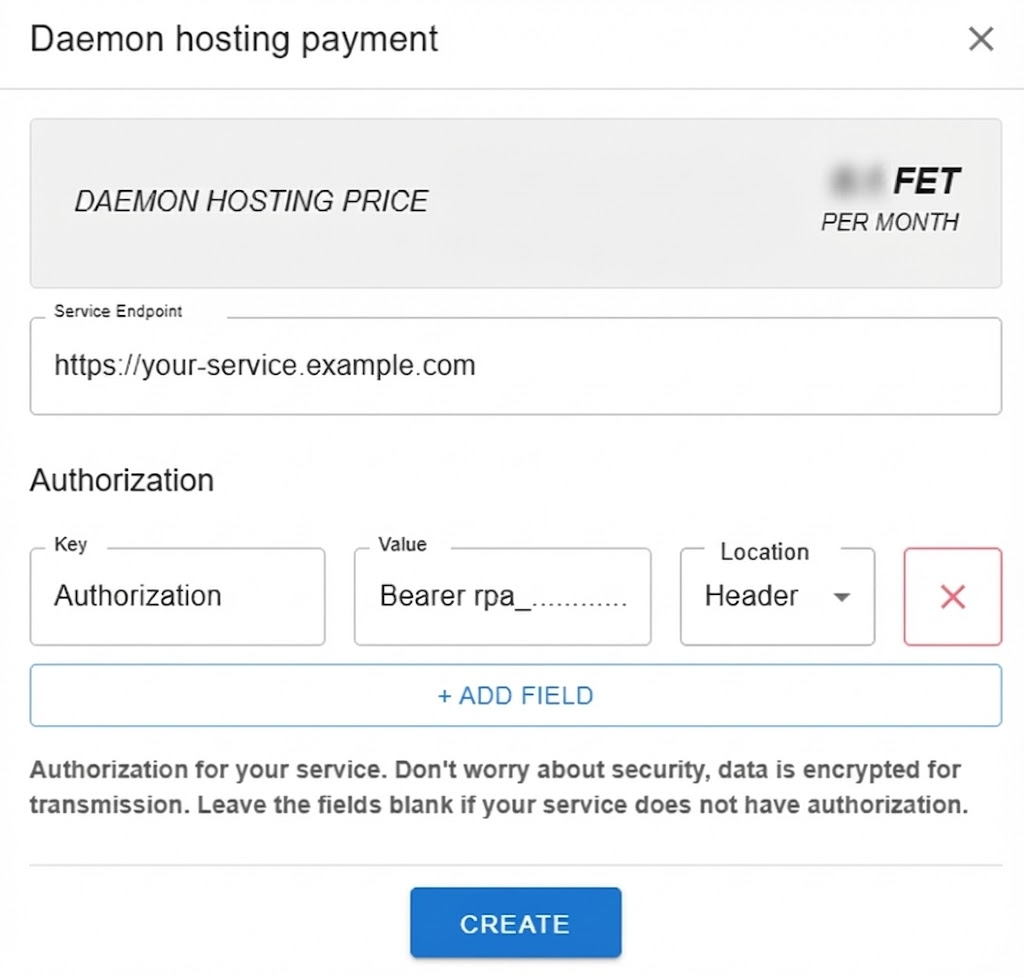
Note: Ensure your Service Endpoint is publicly accessible and properly configured to handle requests from the HaaS daemon.
Step 3: Create and Pay
- Click the Create button after filling in the required fields
- MetaMask will prompt you to confirm the transaction
- Approve the FET token payment for your first month of hosting
The transaction covers:
- Virtual machine provisioning
- Daemon deployment
- ETCD storage setup
- SSL certificate configuration
- One month of hosting service
Step 4: Automatic Configuration
Once payment is confirmed, the platform automatically:
- Provisions dedicated infrastructure
- Deploys and configures the daemon
- Generates and applies SSL certificates
- Sets up payment channel storage (ETCD)
- Populates daemon configuration in your service settings
You'll see these fields automatically filled in your service configuration:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Daemon Endpoint | Public HTTPS endpoint for your hosted daemon |
| Free Call Signer Address | Ethereum address for free call authentication |
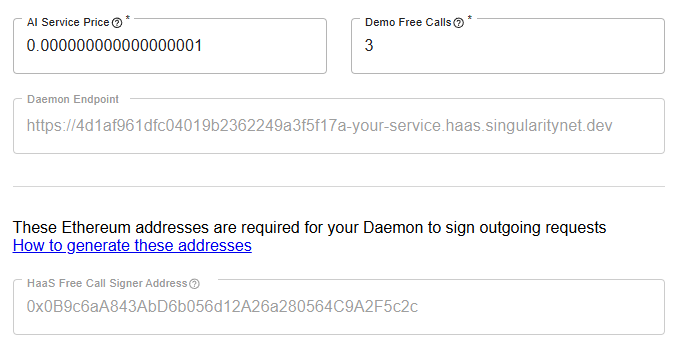
Note: No ETCD configuration required — HaaS uses a managed ETCD cluster automatically.
Note on Screenshot: Ensure Organization ID and Service ID in screenshots follow naming requirements (lowercase, hyphens only, no special characters). Example:
my-company/sentiment-analyzerinstead ofTest_Org/my_service.
Step 5: Complete Service Publication
After HaaS successfully deploys your daemon, complete the remaining service publication steps in the Publisher Portal. Your service is now live with a fully managed daemon infrastructure.
Managing Your HaaS Daemons
Accessing the HaaS Dashboard
Navigate to the HaaS section in the left sidebar of the Publisher Portal to view all your hosted daemons.
Daemon List Overview
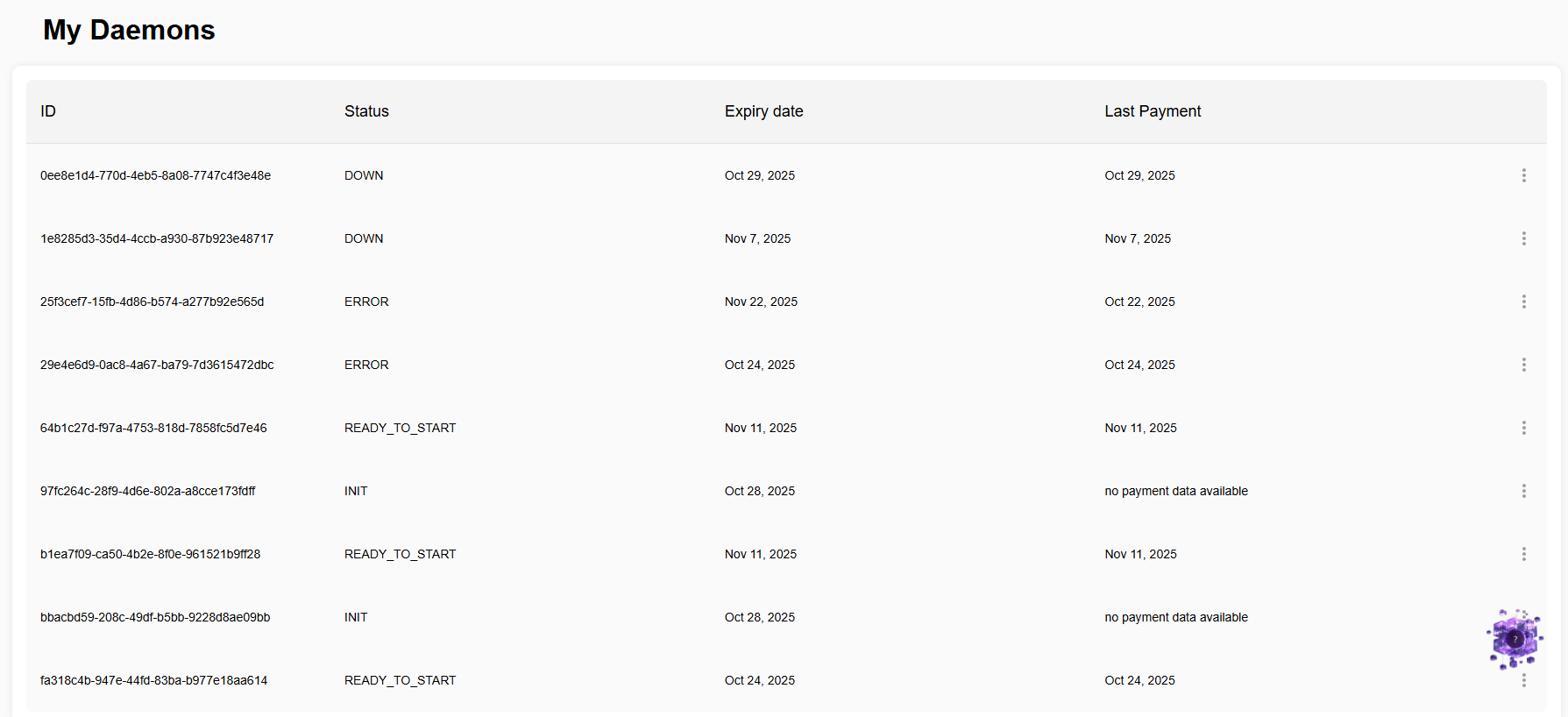
The My Daemons page displays all your HaaS-managed daemons with the following information:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| ID | Unique identifier for the daemon instance |
| Status | Current operational state of the daemon |
| Expiry Date | When your current subscription period ends |
| Last Payment | Date of your most recent payment or "no payment data available" |
| Actions | Management options (three-dot menu) |
Daemon Status Indicators
| Status | Meaning |
|---|---|
INIT | Daemon entity is created, awaiting payment |
READY_TO_START | Payment confirmed, daemon is ready to be deployed |
STARTING | Daemon is being deployed |
RESTARTING | Daemon is being redeployed |
UP | Daemon is deployed and actively handling requests |
DELETING | Daemon is being deleted |
DOWN | Daemon is stopped or subscription expired (not paid) |
CLAIMING | Daemon is temporarily running for one hour to enable fund withdrawal via CLI |
ERROR | Daemon encountered an error during deployment and requires attention |
Daemon Management Actions
Click the three-dot menu (⋮) next to any daemon to access management options:
Top Up
Purpose: Extend your daemon's subscription by paying for additional time.
How it works:
- Click Top Up
- Confirm the FET token payment for the next subscription period
- MetaMask will prompt you to approve the transaction
- Your daemon's expiry date will be extended by the purchased period
Tip: Top up before your expiry date to avoid service interruption.
Detail
Purpose: View detailed information and status history for a specific daemon.
What you'll see:
- Current daemon status
- Full status change history with timestamps
- Configuration details
- Deployment information
- Service endpoint and authorization settings
This page helps you:
- Monitor daemon health
- Track status changes over time
- Debug issues with deployment or connectivity
Update Daemon Config
Purpose: Modify your daemon's service connection and authorization settings.
What you can update:
- Service Endpoint: Change the URL of your AI service if it moves
- Authorization: Update API keys, tokens, or authentication headers
When to use this:
- Your AI service moved to a new domain or port
- You rotated API keys or authentication tokens
- You changed your service's authentication requirements
Important: Ensure your new service endpoint is accessible before updating to avoid downtime.
Run For Claiming
Purpose: Temporarily activate an inactive daemon to enable fund withdrawal from payment channels.
Availability:
- This feature is only available when daemon status is
DOWN - Can be used once every 24 hours (not sooner than 24 hours after the last successful claiming period started)
How it works:
- When your daemon subscription expires, the daemon becomes inactive (
DOWNstatus) - Funds from service calls remain in payment channels on the MPE (Multi-Party Escrow) contract
- To withdraw these funds via CLI, you need signatures from the daemon proving service calls occurred
- Click Run For Claiming to temporarily activate the daemon
- Daemon status changes to
CLAIMINGand runs for one hour - First 2-3 minutes: Daemon is starting up and initializing
- After startup: Use CLI commands to claim funds from payment channels using the daemon's signatures
When to use this:
- Your daemon subscription has expired but you have unclaimed funds in payment channels
- You want to withdraw funds without renewing the full subscription
- You need daemon signatures to complete the claiming process via CLI
Important: This feature activates the daemon for one hour specifically to provide the signatures needed for claiming funds through the MPE contract. The actual fund transfer is performed via CLI commands, not through the HaaS interface. Wait 2-3 minutes after activation before attempting to claim funds.
Payment and Billing
Subscription Model
HaaS operates on a monthly subscription basis paid in FET tokens:
- Payment is required upfront for each month
- The daemon automatically becomes unavailable when the subscription expires
- You can top up at any time to extend the expiry date
- Multiple daemons require separate subscriptions
Important Payment Notes
Subscription Management:
- Monitor your daemon's expiry date in the dashboard
- Top up before expiry to maintain continuous service
- Expired daemons enter
DOWNstatus and stop processing requests - When you top up after expiration, the daemon restarts and the new subscription period begins from the moment of payment
Fund Management:
- Service call payments accumulate in payment channels on the MPE contract
- When your subscription expires, use Run For Claiming to temporarily activate the daemon if you need to withdraw funds via CLI
- Unclaimed funds remain in payment channels and can be accessed using the claiming feature
