Appearance
Introduce in training
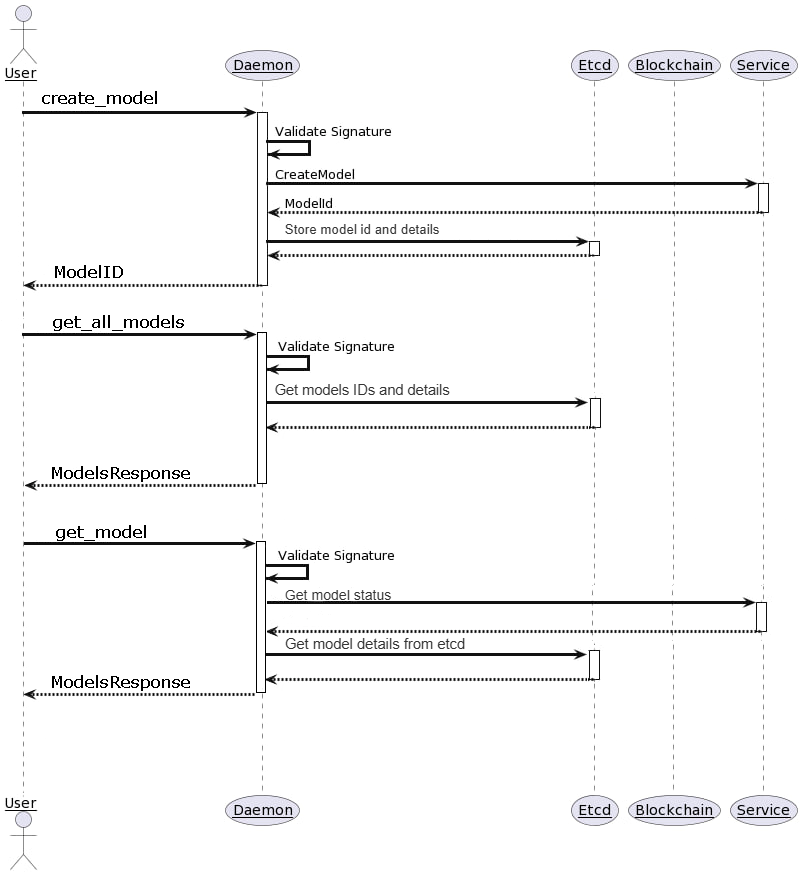
This guide will help you maintain training for your service.
The AI developer needs to implement 8 methods for daemon training.proto
Most of the methods are free, but the methods for validation and training are paid, the price for them can be found through validate_model_price & train_model_price. As a service provider, you must implement the logic of calculating the price for these two methods. You can always return 1 cog or make dynamic logic depending on the parameters and dataset.
AI consumer will call all these methods:
proto
service Model {
// Free
// Can pass the address of the model creator
rpc create_model(NewModel) returns (ModelID) {}
// Free
rpc validate_model_price(ValidateRequest) returns (PriceInBaseUnit) {}
// Paid
rpc upload_and_validate(stream UploadInput) returns (StatusResponse) {}
// Paid
rpc validate_model(ValidateRequest) returns (StatusResponse) {}
// Free, one signature for both train_model_price & train_model methods
rpc train_model_price(ModelID) returns (PriceInBaseUnit) {}
// Paid
rpc train_model(ModelID) returns (StatusResponse) {}
// Free
rpc delete_model(ModelID) returns (StatusResponse) {
// After model deletion, the status becomes DELETED in etcd
}
// Free
rpc get_model_status(ModelID) returns (StatusResponse) {}
}Scheme
Limitations
- Only service type grpc support training;
- You can't change training.proto file.
Step by step
Write your service proto file with training.proto features:
protosyntax = "proto3"; package service; import "training.proto"; message sttResp{ string result = 1; } message basicSttInput { bytes speech = 1; } message sttInput{ // Specify that your method accepts a training.ModelID in order to support training training.ModelID model_id = 1; bytes speech = 2; } service ExampleService{ rpc stt(sttInput) returns (sttResp) { # can specify requirements for dataset option (training.dataset_description) = "Additional requirements"; option (training.dataset_files_type) = "png, mp4, txt, mp3"; option (training.dataset_type) = "zip, tar.gz"; option (training.dataset_max_count_files) = 100; option (training.dataset_max_size_mb) = 100; option (training.dataset_max_size_single_file_mb) = 10; option (training.default_model_id) = "default"; option (training.max_models_per_user) = 5; } rpc basic_stt(basicSttInput) returns (sttResp) { // basic stt method without training support }}Generate gRPC code for your programming language. For example, we will use Python.
Install grpc tools for python:shpip3 install grpcio pip3 install grpcio-toolsThen generate pb files for training.proto and for your service.proto:
shpython -m grpc_tools.protoc -I. --python_out=. --pyi_out=. --grpc_python_out=. training.proto python -m grpc_tools.protoc -I. --python_out=. --pyi_out=. --grpc_python_out=. service.protoImplement and write server logic for model methods. Example:
pythonfrom concurrent import futures import grpc import service_pb2 import service_pb2_grpc import training_pb2_grpc import training_pb2 from training_pb2_grpc import ModelServicer from service_pb2_grpc import ExampleService server = grpc.server(futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=10)) training_pb2_grpc.add_ModelServicer_to_server(ModelServicer(), server) service_pb2_grpc.add_ExampleServiceServicer_to_server(ExampleService(), server) # you should use this endpoint in config daemon: model_maintenance_endpoint server.add_insecure_port("[::]:5002") server.start() server.wait_for_termination() # Your service methods class ExampleService(service_pb2_grpc.ExampleServiceServicer): def basic_stt(self, request, context): # no model_id in request speech_data = request.speech return service_pb2.sttResp(result="RESULT without pre-trained model") def stt(self, request, context): # get the ID of the model that the user wants to use for this method model_id = request.model_id.model_id speech_data = request.speech return service_pb2.sttResp(result="RESULT with model " + model_id) # Model maintaining methods class Training(training_pb2_grpc.ModelServicer): def create_model(self, request, context): print("new model: ", request.name) print("model for grpc_method_name: ", request.grpc_method_name) return training_pb2.ModelID(model_id="NEW_RANDOM_ID") def get_model_status(self, request, context): model_id = request.model_id.model_id return training_pb2.StatusResponse(training_pb2.READY_TO_USE) def delete_model(self, request, context): model_id = request.model_id.model_id return training_pb2.StatusResponse(training_pb2.DELETED) def validate_model_price(self, request, context): print(request.training_data_link) return training_pb2.PriceInBaseUnit(price=1) # 1 cog def train_model_price(self, request, context): model_id = request.model_id.model_id return training_pb2.PriceInBaseUnit(price=1) # 1 cog def train_model(self, request, context): model_id = request.model_id.model_id return training_pb2.StatusResponse(training_pb2.TRAINING) def upload_and_validate(self, request_iterator, context): file_path = "uploaded_file.raw" total_size = 0 with open(file_path, "wb") as f: for chunk in request_iterator: f.write(chunk.chunk) total_size += len(chunk.chunk) print(f"File uploaded: {file_path}, size: {total_size} bytes") return training_pb2.StatusResponse(training_pb2.VALIDATING) def validate_model(self, request, context): model_id = request.model_id training_data_link = request.training_data_link return training_pb2.StatusResponse(training_pb2.VALIDATING)Then run your service and update daemon config:
model_maintenance_endpoint— You can specify a separate endpoint for gRPC server for Model Maintenance like create_model, delete_model, get_model_status, validate_model_price etc;model_training_enabled— need to be true for training.Restart daemon
Test and call model methods via SDK, for example: Python SDK
