Appearance
State Service Calls
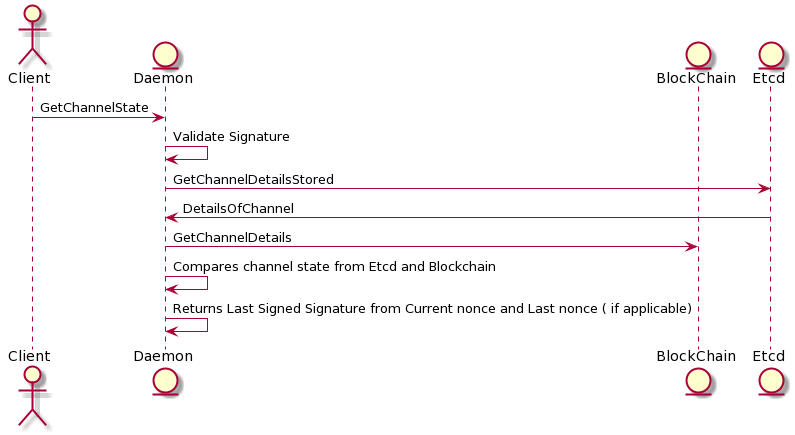
As the name suggests, this call will be used by the client to determine the next amount to sign to make a service call.
Daemon keeps track of the off chain state of the channel Details involve Channel Id Nonce,Amount signed , Signature and the nonce of the channel , and in order to sign the amount for the next call, the client needs to know the amount it had last signed (X), the new call will be signed with an amount X + P , where X is the last signed amount and P is the price
Daemon also sends back the last signed signature of the old nonce ( in case a claim is in progress or a claim was made)
Pay Per use calls
The client signs in for the next cumulative amount ( i.e X+P), where X is the amount last amount signed on the given Channel Id and Nonce
Free Calls
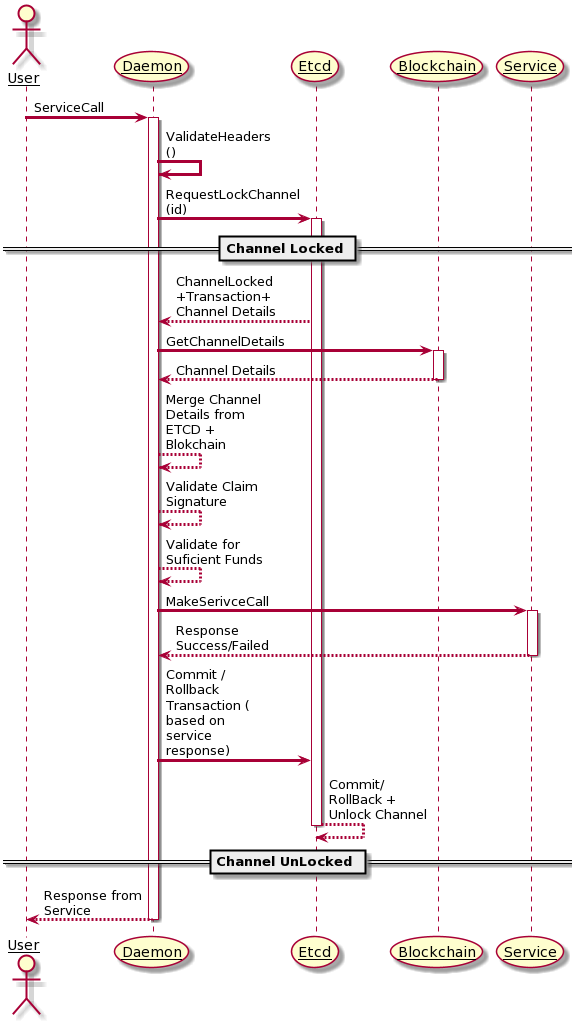
How many free Calls are Left ?
As a service provider one may wish to provide free calls . However you need some validations to ensure , that only authorized users can make this call and as a service provider you would want to restrict the number of such free calls made. To even check if free calls are allowed, you need to send in Daemon a signature and a token
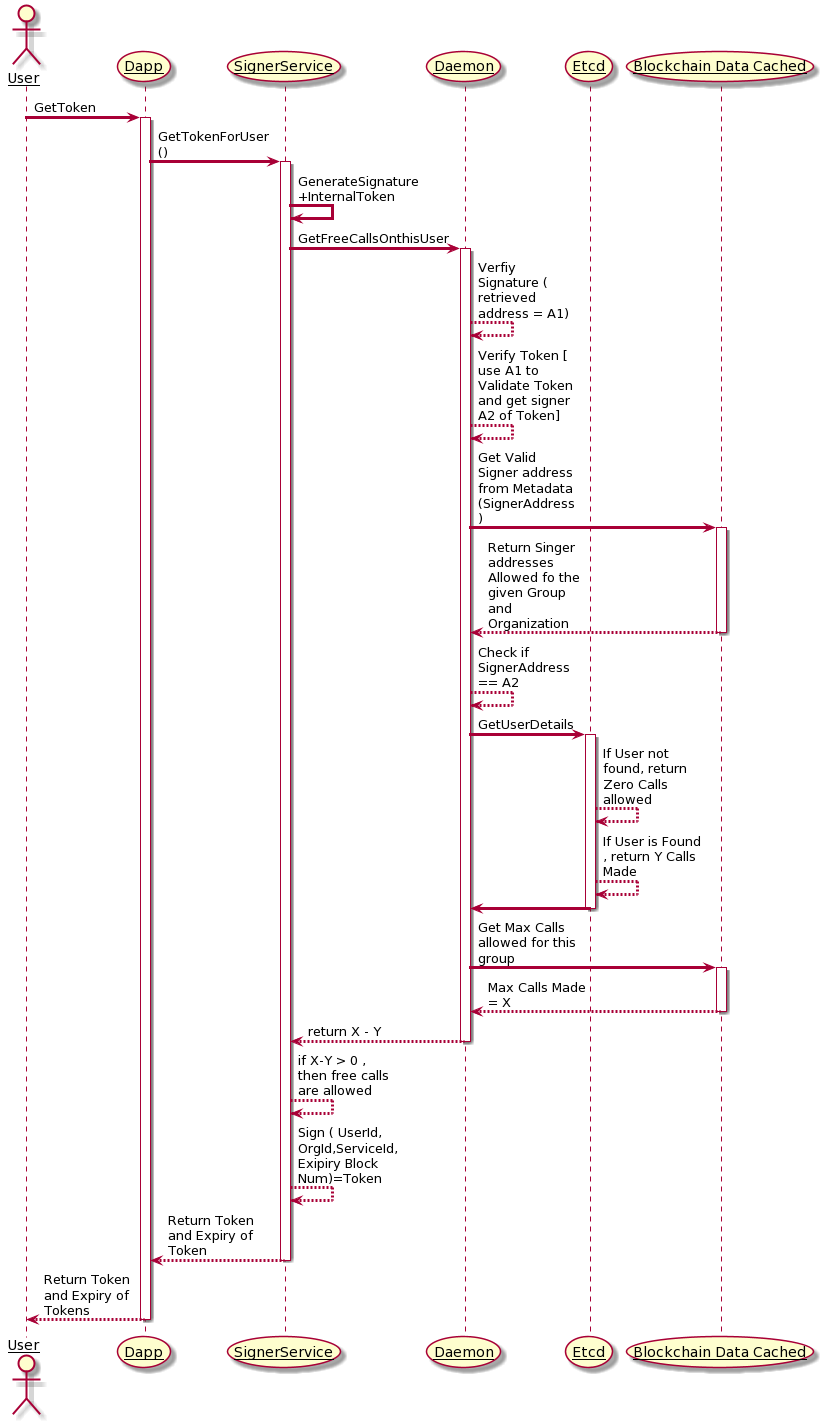
Making an Actual Free Call
If the Signatures are valid,Daemon increments the usage count by 1. The Signature validations and authentication is exactly the same as explained , just that the ETCD State is upated with usage accordingly
Control Service Calls
Please note, Daemon doesnt do any claims on blockchain, it is responsible ONLY for maintaining the states. Actual claims can done using snet-cli/publisher portal Daemon provides a bunch of grpc calls to retrieve data the service provider needs to make claims on block chain. Keeps track of claims in Progress. One can view all the data using cli commands in snet-daemon
No write operation on block chains are done by Daemon (will be take care of by the snet client ), Finish on the claim(reset channel amount used to zero!) should be called only after the payment is successfully claimed and block chain is updated accordingly. One way to determine this is by checking the nonce in the block chain with the nonce in the payment,for a given channel if the block chain nonce is greater than that of the nonce from etcd storage => that the claim is already done in block chain. and the Finish method is called on the claim.
List-unclaimed requests
As a first step the service provider needs to be aware of all the unclaimed money Service Provider needs to send the following message (using snet-cli/publisher portal): mpe_address, current_block_number, signature(“__list_unclaimed”, mpe_address, current_block_number)
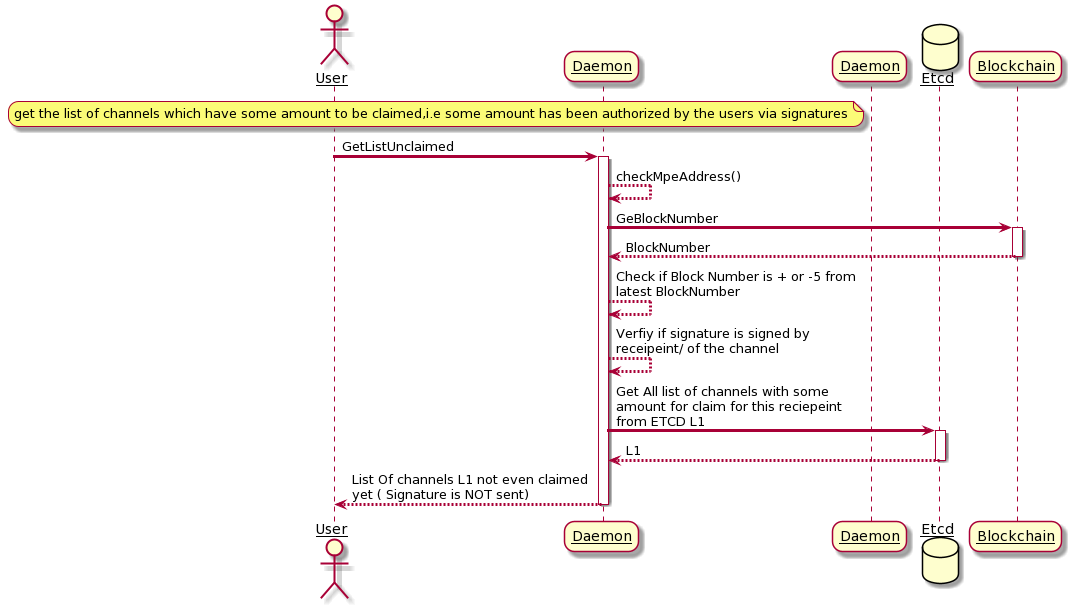
After receiving this message, daemon does the following: Verify that mpe_address is correct Verify that actual block_number is not very different (+-5 blocks) from the current_block_number from the signature Verify that message was signed by the service provider (“payment_address” in metadata). Send list of unclaimed payments without signatures (we don’t send signatures here just to be safe!!!)
Start-claim request/requests
using snet-cli the following message: mpe_address, channel_id, signature(“__start_claim”, mpe_address, channel_id, channel_nonce)
After receiving this message, daemon does the following: Check that current channel nonce in blockchain is equal to nonce of the channel in etcd. It means that all previous payments on this channel was claimed already. Daemon should remove all payments with nonce < channel_nonce from payment storage. Verify that signature is authentic ( “payment_address” is in metadata !) Increase nonce in storage and send last payment with old nonce to the caller (snet-cli/publisher portal)
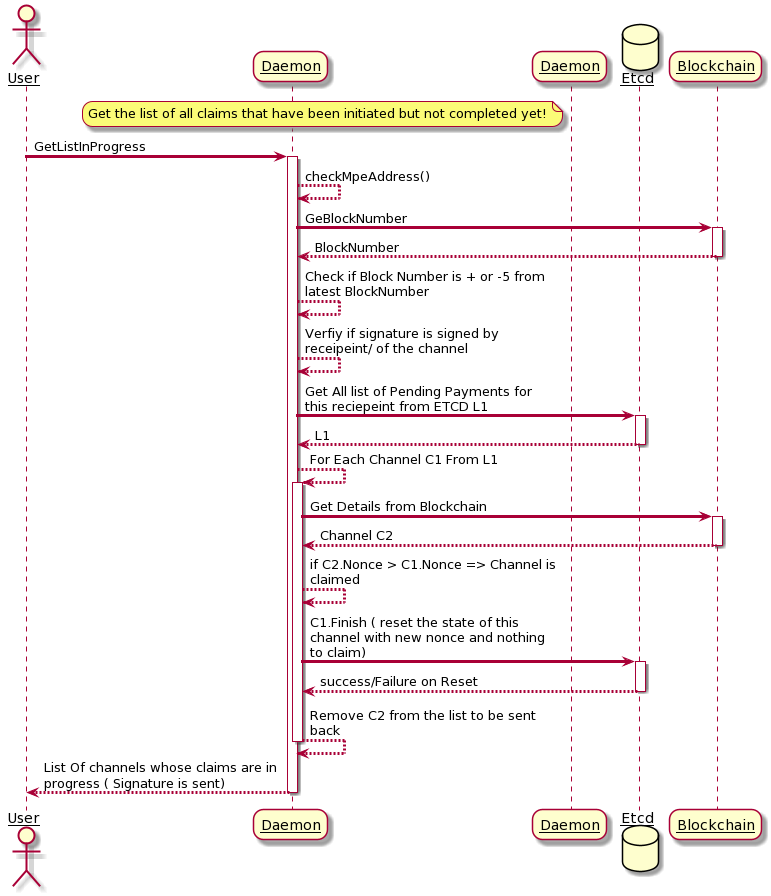
List-in-progress
Get the list of all claims that have been initiated but not completed yet Before sending a list of payments, daemon should remove all payments with nonce < blockchain nonce from payment storage (call finalize on them?). It means that daemon removes all payments which were claimed already.
Signature Details
For exact details on signatures please refer to snet-daemon
